Describe the Matrix of Connective Tissue
AnswerConnective tissue is made up of fibrous layers of protein and has an extracellular matrix. Generally connective tissues are made up of cells and the extracellular matrix that they produce.
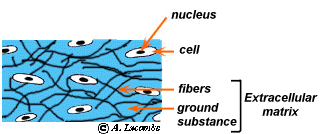
Al S Tutorial Histology Connective Tissues General Features Functions
The function of this type of tissue is to provide structural and mechanical support for other tissues and to mediate the exchange of nutrients and waste between the circulation and other tissues.
. These cells also secrete modified polysaccharides which accumulate between cells and fibres and act as the matrix ground substance. The matrix plays a major role in the functioning of this tissue. Some are classified as dense connective tissue proper and have a dense arrangement of extracellular protein fibers that give the tissue strength and toughness.
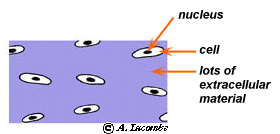
The extracellular matrix of the blood is called blood plasma. A type of cell found in connective tissue that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen. Extensive protein fibers in the extracellular matrix.
It is the most widespread tissue of the body and can be found in every organ. Composed mainly of nonliving extracellular matrix that separates the cells of the tissue. Extracellular matrix is defined as the noncellular components of connective tissue.
Matrix is similar to areolar all 3 fiber types but it is very sparse. The matrix of connective tissues consist of living cells and a non-living substance called as the ground substance. What are the cells of blood tissue.
Describe the matrix of blood tissue. It is composed of variety of cells fibre non-living products of cell and semi-solid matrix between cells. Nonetheless there is still a great variety among the subcategories of connective tissue proper.
Two major components of the matrix are ground substance and protein fibers. Fluid matrix called plasma. Tendons connecting muscles to bone and ligaments connecting bone to bone.
The primary elements of connective tissue include a ground substance fibers and cells. Connective tissue functions in support binding storage and the transport of nutrients. Connective tissue ranges from avascular to highly vascular.
As all connective tissue it has cellular and extracellular components. Connective tissues are made up of a matrix consisting of living cells and a non-living substance called the ground substance. 4 Two classic functions of connective tissues are mechanical support for bone and soft tissues and intercellular exchange of oxygen blood water gases cells and wastes.
Extracellular material of a tissue. In contrast to epithelia connective tissue is sparsely populated by cells and contains an extensive extracellular matrix consisting of protein fibers glycoproteins and proteoglycans. 4 rows The purposes of this update are to provide an overview of the composition structure and function.
The proportions of these components vary from one part of the body to another depending on the local structural requirements. The ground substance is made of an organic substance usually a protein and an inorganic substance usually a mineral or water. Characteristics of connective tissue.
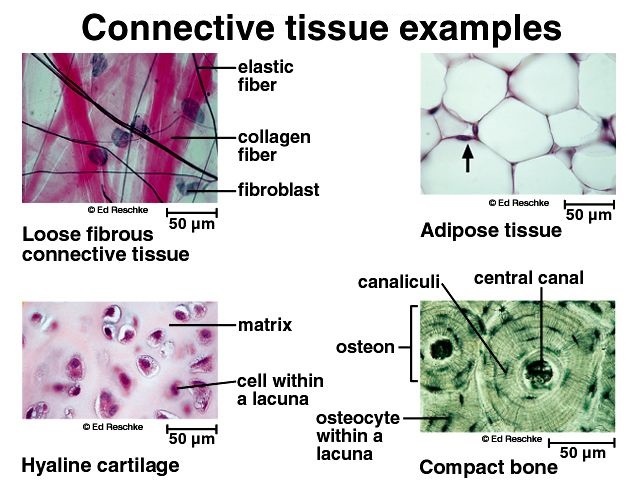
In all connective tissues except blood the cells secrete fibres of structural proteins called collagen or elastin. The cells also secrete a thin gel of polysaccharides which together with fibres make matrix or ground substance. Name the 10 types of connective tissues-Areolar Tissue-Reticular Tissue-Dense Regular Connective Tissue-Dense Irregular Connective Tissue-Adipose Tissue-Hyaline Cartilage.
The ground substance is made up of organic substance like proteins and inorganic substance like minerals and water. Composed of tissue fluid. The principal cell of connective tissues is the fibroblast.
Connective tissue is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix that binds the cells and organs integrating all parts of the body. Components of connective tissue All forms of connective tissue are composed of 1 extracellular fibres 2 an amorphous matrix called ground substance and 3 stationary and migrating cells. It consists of water and solutes proteins electrolytes nutrients.
Describe the origin and basic function of connective tissue Discuss the basic structure and function of ground substance properties such as proteoglycans GAGs and multi adhesive proteins Discuss the functional relationship of transmembrane proteins have to glycoproteins to allow for adhesion of cells to the extracellular matrix. Connective tissue is made up of a few cells present in the intercellular framework of protein fibres secreted by the cells known as collagen or elastin. Blood is the specialized connective tissue within the circulatory system that transports blood cells and dissolved substances throughout the body via blood vessels.
The fibres provide strength elasticity and flexibility to the tissue. Explain what the matrix of a connective tissue is and describe its components. What are the fiber types found in the extracellular matrix of adipose connective tissue.
Unlike epithelial tissue which has cells that are closely packed together connective tissue typically has cells scattered throughout an extracellular matrix of fibrous proteins and glycoproteins attached to a basement membrane. Cells of the connective tissue are suspended in a non-cellular matrix that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. The matrix usually includes a large amount of extracellular material produced by the connective tissue cells that are embedded within it.

Connective Tissues Biology For Majors Ii

Connective Tissue Flashcards Quizlet
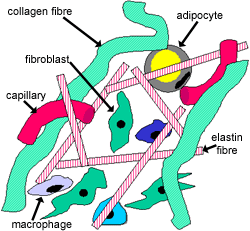
Connective Tissue The Histology Guide
Embryonic Connective Tissue Connective Tissue Proper Specialized Connective Tissue Science Online

8 9 Connective Tissue Name Elements Of The Ecm Extra Cellular Matrix Kinds Of Ct Fibers Functions Describe Ct Ground Substance How It Can Vary In Diff Ct S 9

Schematic Representation Of Two Connective Tissues A Dense Regular Download Scientific Diagram

Connective Tissue The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Connective Tissue Connective Tissue Is Responsible For Providing Structural Support For The Tissues And Organs Of The Body Connective Tissue Is Composed Ppt Download
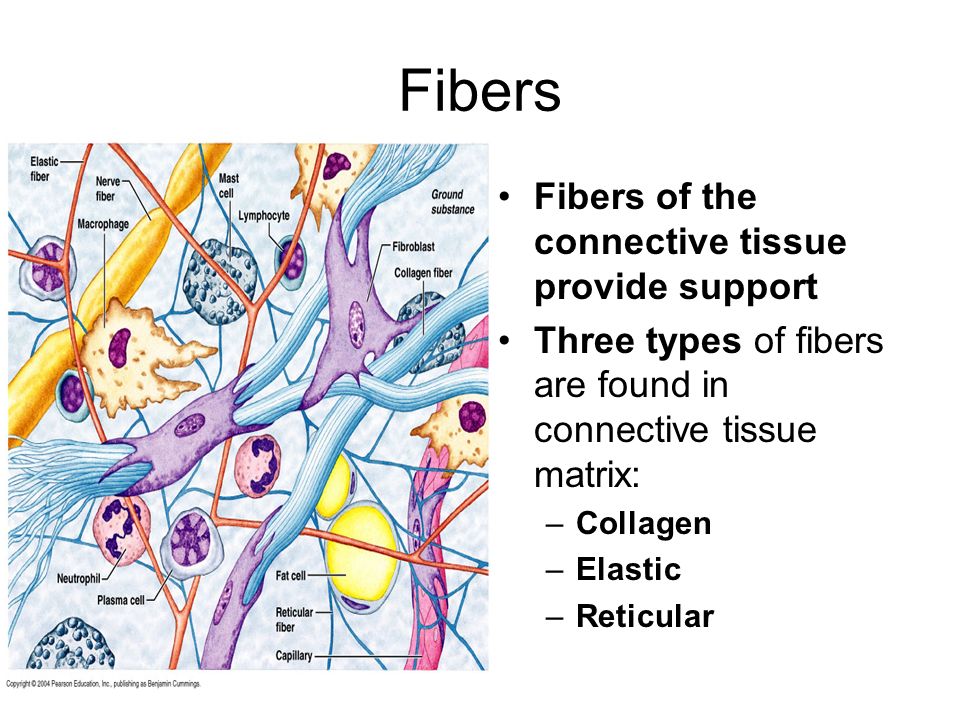
What Are The Three Main Types Of Fibers Found In The Matrices Of Connective Tissues Socratic

Connective Tissue Supports And Protects Anatomy And Physiology I

Connective Tissue The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Schematic Representation Of Two Connective Tissues A Dense Regular Download Scientific Diagram
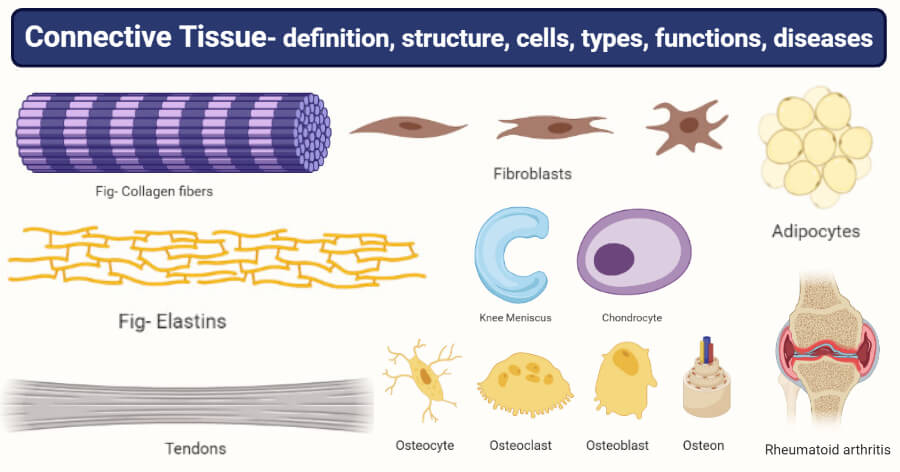
Connective Tissue Definition Structure Cells Types Functions Diseases

Al S Tutorial Histology Connective Tissues General Features Functions

Connective Tissues Biology For Majors Ii

4 3 Connective Tissue Supports And Protects Anatomy Physiology
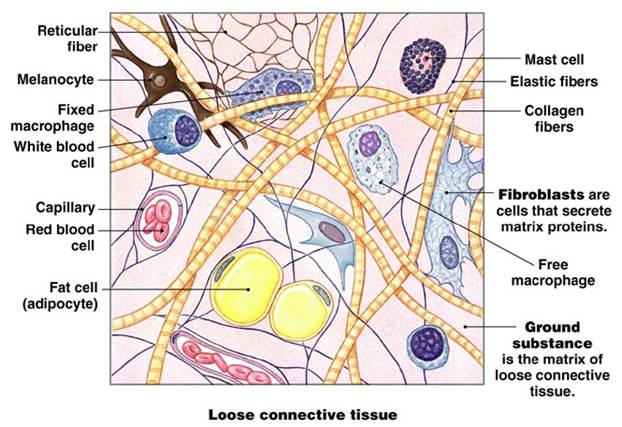
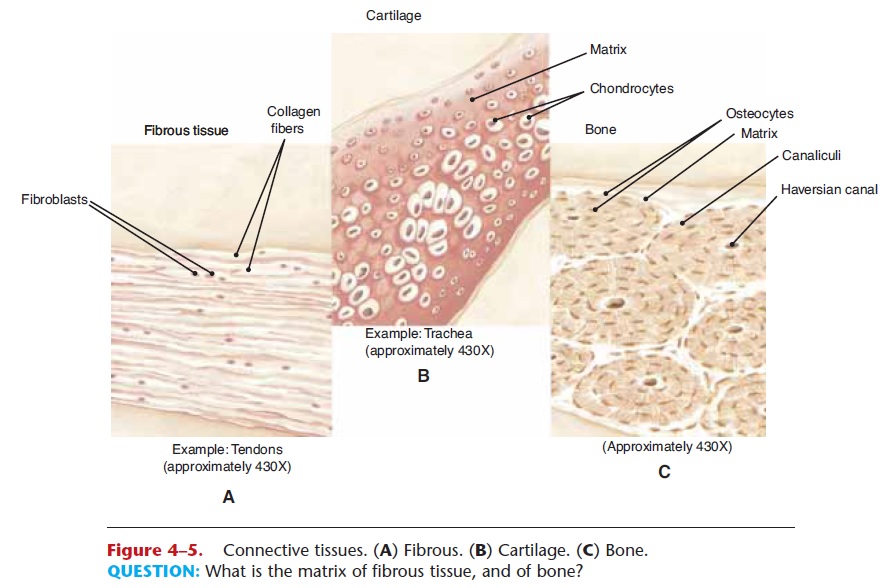

Comments
Post a Comment